Dry and wet Injections Manufacturing
Best innovations in metallurgy
Dry and wet injections manufacturing requires strict adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), compliance with regulatory guidelines, and robust quality control systems to produce safe and effective injectable medications.
These manufacturing processes ensure accurate dosing, sterility, and stability of the injections, enabling healthcare professionals to administer medications through the parenteral route for rapid and precise therapeutic outcomes.
Dry Injections Manufacturing:
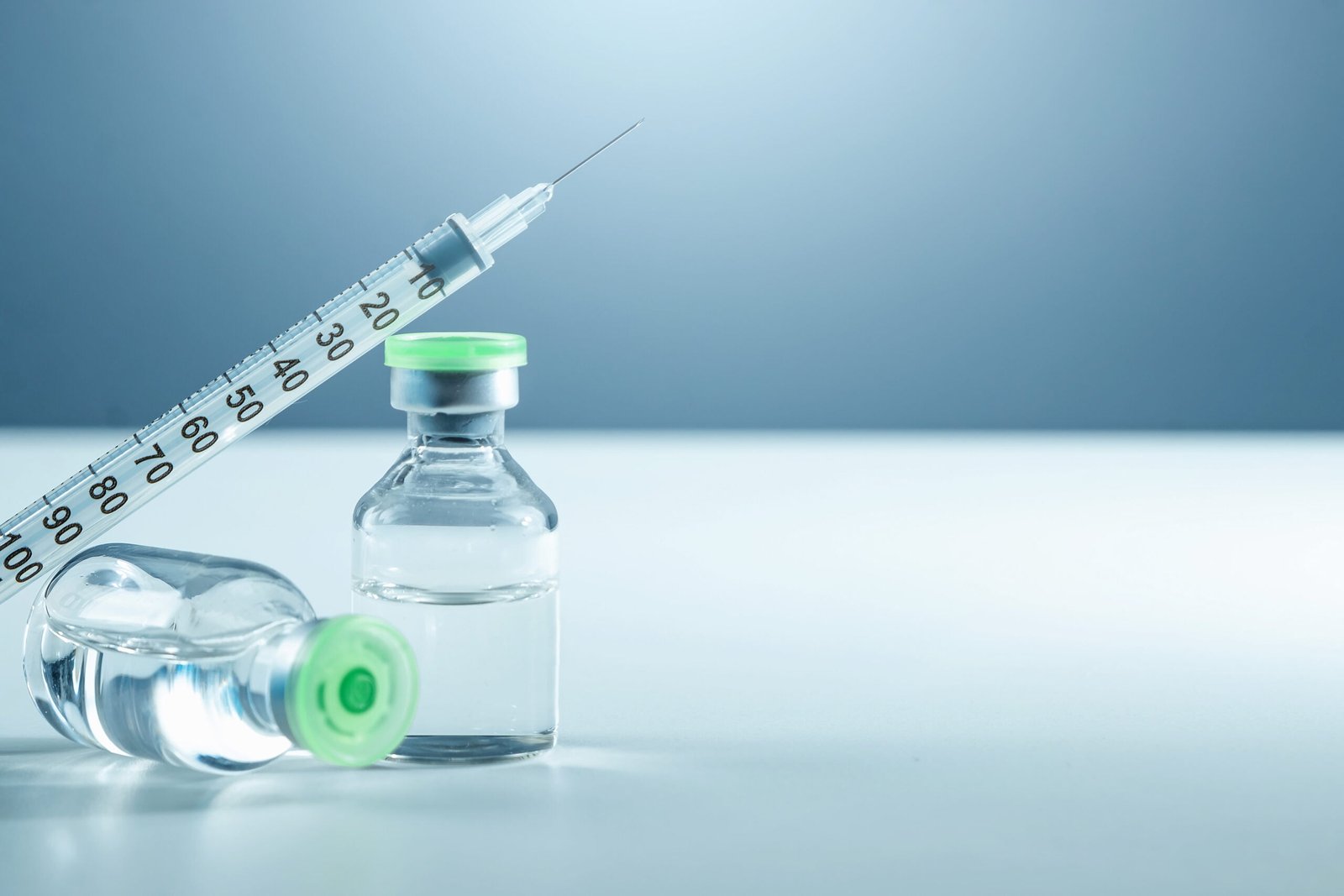
Dry Powder Form: Dry injections are formulated as powders that are reconstituted with a suitable diluent before administration. The dry powder is typically a mixture of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and various excipients such as stabilizers, bulking agents, and buffers.
1. Dry Injections Manufacturing:
Dry Powder Form: Dry injections are formulated as powders that are reconstituted with a suitable diluent before administration. The dry powder is typically a mixture of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and various excipients such as stabilizers, bulking agents, and buffers.
- Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process for dry injections involves steps such as API synthesis or sourcing, formulation development, blending, granulation (if necessary), drying, milling, and final powder filling into vials or ampoules.
- Sterilization: Dry injection powders are typically sterilized using techniques such as terminal sterilization (e.g., autoclaving) or aseptic processing to ensure the sterility of the final product.
2. Wet Injections Manufacturing:
- Liquid Formulation: Wet injections are manufactured as ready-to-use liquid formulations, eliminating the need for reconstitution. The liquid formulation can be aqueous-based, oil-based, or a combination of both, depending on the solubility and stability requirements of the drug.
- Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process for wet injections involves API synthesis or sourcing, formulation development, blending, filtration, sterilization (e.g., through terminal sterilization or aseptic processing), and filling into vials or ampoules. The liquid formulation may undergo additional steps such as lyophilization (freeze-drying) if it needs to be reconstituted later.
- Quality Control: Strict quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to ensure the sterility, uniformity, and stability of the liquid formulation. This includes testing for particle size, pH, sterility, endotoxin levels, and other relevant quality attributes.
3. Packaging and Quality Assurance:
- Packaging: After the injections are manufactured, they are typically filled into sterile glass vials or ampoules. The vials or ampoules are sealed with closures, such as rubber stoppers or flip-off caps, to maintain the sterility of the product. The filled vials or ampoules are then labeled with appropriate product information, including dosage strength, batch number, expiry date, and usage instructions.
- Quality Assurance: Throughout the manufacturing and packaging processes, rigorous quality control and quality assurance measures are implemented to ensure that the injections meet the required standards for safety, efficacy, sterility, and stability. This includes regular testing and analysis of samples from each batch to ensure compliance with established specifications.
- Abdur Rashid
Project Information
Completely synergize resource taxing relationships via premier.
